Often, at a meeting, I am asked by small business owners to review their website and give them my thoughts. These are a few common issues with websites, especially DIY websites. These are good tips on what to look for when doing a DIY website.
- Images missing alternative (alt) text
- Insufficient color contrast
- Improper heading structure
- Images are too large
- Missing SSL certificate
Images missing alternative (alt) text
Alt text is text used to describe an image on a website. It is used mostly by people with vision disabilities who use screen-readers to read the content of a website. When screen-readers get to an image, it will read the text out loud. Most people I talk to have no idea what alt text is. Most websites that I see that were created by business owners don’t include alt-text.
Missing alt-text can have the following negative effects:
- Your images may not be found by search engines. Images with alt-text can help search engines better understand your website and possibly improve your overall search engine optimization (SEO).
- You could be missing out on sales from an underestimated population.
- You could be making life harder for someone with a disability.
Want to know more about alt-text? We wrote an article on it: What is alt-text and why should you use it.
Insufficient color contrast
Your content will be much harder to read if you do not have sufficient color contrast. Color blindness affects about one in twelve men and about one in 200 women. These people may have a very difficult time with your website if you do not have enough contrast between components such as text and background. Beyond color-blindness, having the wrong colors can cause eye fatigue and cause people to stop reading your content.
Our favorite tool for testing color contrast is the WebAIM color contrast checker.
Improper heading structure
In Hyper-Text Markup Language (HTML) – the computer language used on all websites – headings are indicated with “h” tags (h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, and h6). When your web browser displays these h tags, the headings are usually displayed in different sizes automatically based on heading level. H1s are displayed larger than h2s, h2s are larger than h3s, and so on. If you are using a Content Management System (CMS) such as WordPress, then the theme’s stylesheet probably makes the headings different sizes based on the heading level as well. For this reason, people often use different heading levels to control the size of the headings.
The proper way to control heading size is to use Cascading Style Sheets (CSS). If you are using a CMS, you are usually given some size adjustment options via a slider or a dropdown menu.
Headings help search engines to understand page and topic structures. There should only be one h1 per page – usually the page title. The h1 should be followed by an h2. You can have multiple h2 headings on a page and these should be subtopics of the h1. H3s should only come after h2s, h4s after h3s, and so on.
Images are too large
Slow websites can affect a website visitor’s experience. If the website is too slow, people will leave your page and may not view the content you want them to see. One of the most common reasons for a slow website is having excessively large images on the page. While large, high-definition images may be stunning, they are rarely ever necessary for an effective website.
We suggest using optimized images of the right size for where it is being used. If you were inserting an image with a maximum width of 1080px on the website, your image width should probably be between 1080px to 1200px. There are many tools to resize images such as Adobe Photoshop or Imageresizer.
Missing Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate
Installing an SSL certificate on your web server (your hosting provider) is a way to ensure communication between the web server and a web browser (Chrome, Edge, Firefox, etc.) is encrypted. These digital certificates are issued by a Certificate Authority (CA). It is a semi-complicated procedure that gives your website a secure designation.
When you have a secure connection via an SSL certificate, you will usually see a padlock in the URL address bar. If you don’t have an SSL certificate, people visiting your website may see a warning from the browser stating that your website is not secure. If people visit your website and quickly leave because it is marked as insecure (commonly referred to as the bounce rate), search engines may decide not to show your website in the search results.
This is an example of what it looks like when you don’t have an SSL certificate:

This is an example of what it looks like when an SSL certificate is installed:
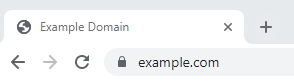
These days, there is really no reason why your website should not have an SSL certificate. Most web hosts provide a free SSL certificate for every website. If they don’t, that is a good indication that you should change your web hosting provider. Need help choosing good hosting? Read our article on WordPress hosting companies.
Conclusion
In our work we often review websites and find many of the same common issues. Optimizing your website can lead to better usability and better results in the search engines.
Are we missing any common issues that we should include? Let us know in the comments below.
We hope you find this content useful. Please reach out to us if we can help you fix these issues or help you to improve your online presence.

